Haze Metrics Converter
Note: 3 converters are given below, dependent on input (VR, bext, and DV).
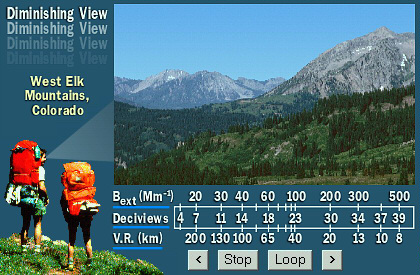
Caution: The converters cannot be used for average values. E.g. you cannot calculate average DV from average bext; instead, you must calculate DV for each daily measurement, and then calculate an average DV from the individual DV values.
Visual Range (V.R.):The greatest distance at which an observer can just see a black object viewed against the horizon sky.
Units: Distance, e.g. kilometers (km)
Benefit: This metric is most useful in situations where only the distance that one can see is important, such as for aviation.
Drawback: Does not account for changes in scene, such as loss of textures and discoloration as haze increases.
Relationships:
V.R. = K/bext
Where K is the Koschmieder Coefficient – the natural log of the contrast threshold of the human eye, K = 3 – 3.9.
Note that a unit conversion is required in converting between V.R. and bext.
Light Extinction (bext): The attenuation of light due to scattering and absorption as it passes through a medium.
Units: inverse distance, e.g. inverse mega meters (Mm-1)
Benefit: Light extinction can be directly related to gaseous and aerosol concentrations.
Drawback: Light extinction is non-linearly related to a person’s perception of changes in haze. For example, a 10 Mm-1 increase in bext will have a larger perceived impact on a scene at bext = 20 Mm-1 than at bext = 100 Mm-1
Relationships:
bext = K/V.R.
bext = 10*exp(DV/10); where bext is calculated in Mm-1.
Where K is the Koschmieder Coefficient – the natural log of the contrast threshold of the human eye, K = 3 – 3.9.
Note that a unit conversion is required in converting between V.R. and bext.
Deciview (DV): A metric of haze proportional to the logarithm of the atmospheric extinction (bext).
Units: Unitless
Benefit: Under many circumstances a change in one deciview will be perceived to be the same on clear and hazy days.
Drawback: Deciview is not easily related to gaseous and aerosol concentrations
Relationships:
DV = 10*ln(bext/10); where bext is expressed in Mm-1.
Perceived Visual Air Quality (PVAQ): An index that relates directly to how human observers perceive changes in visual air quality.
Units: Unitless
Benefit: Quantitatively, measures haze or visibility impairment to how human observers perceive changes in visual air quality.

